A Must for Car Manufacturers: The 84th International Motor Show in Geneva
The Geneva International Motor Show in Geneva (March 6 – 16, 2014) was a huge success, with over 670,000 attendees.
Every year, the show attracts journalists, buyers and automotive industry representatives from around the world. One of the world’s best major automotive shows, showcasing new models, new trends, new technologies and concepts of all aspects in the automotive industry.
The show is divided into seven separate areas, with the auto manufacturer’s area being the most popular. With nearly every make, model, fuel type, economy to luxury represented there was something to satisfy every enthusiast taste.

Overview Hall 4
This year the Peugeot 308 won the award “Car of the Year”. This international award is considered to be one of the most prestigious and desirable car award in the world, decided by jury of 58 journalists from 22 European countries.
Next year the Geneva International Motor Show will take place from March 5 – 15, 2015. For more information, please visit the fair website here.
Julian Busch, CEO of China Certification Corporation, took the opportunity to visit the Geneva International Motor Show to assess future market developments in the automotive industry. There were plenty of opportunities to discuss the CCC certification for the Chinese market with the manufacturers and suppliers that were exhibiting, along with current clients and interested attendees.
China Certification Corporation offers CCC certification for both suppliers and manufacturers. For automobile manufacturers, we can assist them with complete (whole) car approval, which will enable sales of vehicles into the Chinese market.
For automotive suppliers, we will first determine whether a CCC certification is required or possible for certain products or vehicles. Our close relations with Chinese certification authorities allow us to obtain a reliable results.
Next, we will determine the best CCC strategy for the approval of the car model(s), with emphasis on the expected sales volume in China. Here there are three different alternatives for applying for the approval:
- Full CCC certification of the vehicle
- Non-mass production CCC for particular vehicle model(s)
- Application for low volume CCC exemption.
We can provide you with complete information so you can determine the best solution, maximizing your return on investment.
We can also support automotive manufacturers to organize the CCC certification of their suppliers. If the car manufacturer centrally coordinates the CCC certification of their suppliers, they can save significant amounts of money.
One of the advantages of using China Certification Corporation is that we manage all of communications with the CQC (China Quality Certification Centre, chin. „中国质量认证中心“), the CCAP (China Certification Centre for Automotive Products, chin. „中汽认证中心“) and other relevant Chinese authorities and test laboratories. In addition, we monitor the GB Standards, implementation rules and other pertinent Chinese regulations to keep our clients informed and in compliance.
Information regarding CCC certification, the certification process and the costs can be found on our website. You will also find details regarding our certification package can be found on our website including a general anticipated time frame. Take a look at our references section for a list of some of our clients and what they are saying about us. For more detailed information please download our free booklet “CCC Made Easy” here. You may also consider our book “A Brief Guide to CCC: China Compulsory Certification”, which can be ordered directly on Amazon here.
Please do not hesitate to call or email with any questions you may have.
New Chinese Test-Standard for Energy-conservation Certification Rules for Flat Panel Televisions
The Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC, Chinese: 国家标准化管理委员会) made an official announcement (announcement No. 9-2013) of a new GB Standard for flat panel televisions (GB Standard 24580-2013) that was published on June 9th, 2013.
This new GB Standard (GB stands for Guobiao, Chinese for National Standard) regulates the minimum allowable values of Energy Efficiency and Energy Efficiency Grades for Flat Panel Televisions and it was implemented, and enforceable as of October 1st, 2013. The new GB standard replaced the previously relevant GB Standard 24850-2010.
To maintain certification for Energy Efficiency and Energy Efficiency Grades for Flat Panel Televisions the following rules apply:
- Initial energy-saving certification must be performed in accordance with the new GB Standard 24580-2013. The CQC will no longer issue certificates that are not in compliance with the new standard.
- Manufacturers which already hold a certificate for flat panel televisions energy-conservation will need to re-submit a change application that shows compliance with the new standard.
- Certificate changes need to be completed by October 1st, 2014. In the event that existing certificates are not changed stating the new standard of compliance by this date, the certificate will be suspended by the authority. If the holder of the certificate fails to resolve their non-compliance by January 1st, 2015, the certificate will be revoked.
The China Quality Certification Center (CQC) also released a new standard of energy conservation certification rules (CQC31 – 452631-2013) for flat panel televisions, which replaces the previously relevant standard CQC31 – 452631-2009.
The modified provisions of the Standard (CQC31 – 452631-2013) call for both conservation during the manufacturing process as well as energy-saving while the flat panel is in operation. It is important to note, that the CQC also added new requirements for external power supplies and new rules for the positioning of the marking of the certified products.
The Chinese certification authorities regularly publish GB standard updates and other certification requirements. These official announcements are often made without any advanced notice and are published only in Chinese language, so please check our website regularly for up to the date and breaking news.
You will find information about official notices regarding this matter in our “News” section on our website. Our close relationships with the certifying authorities allow us to provide you with these updates first, many times before they are officially announced or implemented.
General information regarding CCC certification, CEL certification or CFDA for medical devices can be found on our website.
Please do not hesitate to call or email with any questions you may have.
CCC: Confirmed and extended China compulsory certification for fire protection and fire control products
On January 28, 2014 an important announcement was published on the website of the CNCA (Certification and Accreditation Administration of the People’s Republic of China / Chinese: 中国国家认证认可监督管理委员会). It is regarding an extension of the official CCC product catalogue, requiring CCC for specified fire protection devices as of September 1, 2015. Affected products may no longer be imported, produced, traded, sold or used in any business activities in China without being CCC certified after this date. Also, the announcement confirms and underlines again that CCC is needed for certain fire prevention products.
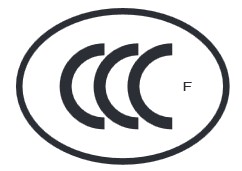
In regards to the CCC logo, there are particular specifications that must be observed carefully. Besides meeting the required ratio of the “3 C” for “China Compulsory Certification”, the logo must also have the abbreviation “F” for “Fire-fighting products”:
According to the official announcement, the following products will require CCC certification in the future, respectively already require CCC certification:
- Fire detectors and alarms
- Fire doors and fire glass for buildings
- Equipment for fire department, e.g. extinguishing devices and fire hoses
- Portable fire extinguishers
- Hydrants
Emergency lighting used in case of fire, fire safety signs, fire alarm devices and respirators will also be included in CCC product catalogue, with more to be added later.
Fire Control Law of the People’s Republic of China, (Chinese: 中华人民共和国消防法) and The Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on Certification and Accreditation, (Chinese: 中华人民共和国认证认可条例) stated that the decision to add these products to the catalogue was made due to legislative issues. Supplemental Implementation Rules and GB Standards (GB stands for Guobiao, Chinese for National Standard) will be published soon.
The GB Standards define the certification need, and the Implementation Rules state the prescribed method of obtaining the certification and required marking of the product with the CCC logo.
You will find information about official notices regarding this matter in our “News” section on our website. Our close relationships with the certifying authorities allow us to provide you with these updates first, before they are officially announced or implemented.
The extension of CCC compulsory certification for fire protection products was published jointly by three Chinese authorities: The Ministry of Public Security of the People’s Republic of China (MPS, Chinese: 中华人民共和国公安部), the CNCA and the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ, Chinese: 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局局).
This year, the Chinese authorities have already published several new changes regarding the regulatory framework of CCC certification. Among these is the update of the Chinese GB Standard for seat belts (GB 14166-2013 “Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and ISOFIX child restraint systems for occupants of power-driven vehicles”). September 1, 2014, CCC certification for child safety seats will become mandatory.
These official announcements are often made without any advanced notice and are published only in Chinese language, so please check our website regularly for up to the date and breaking news.
Information regarding CCC certification, the certification process and the costs can be found on our website. You will also find details regarding our certification package can be found on our website including a general anticipated time frame. Take a look at our references section for a list of some of our clients and what they are saying about us. For more detailed information please download our free booklet “CCC Made Easy” here. You may also consider our book “A Brief Guide to CCC: China Compulsory Certification”, which can be ordered directly on Amazon here.
Please do not hesitate to call or email with any questions you may have.
NAL: Mandatory NAL approval for telecommunications products for the Chinese market
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) of the People’s Republic of China was established in 2008. The MIIT is responsible for the management of public telecommunication networks in the P.R. China and also manages the certification of telecommunication devices. The MIIT is also responsible for the “Network Access License” (NAL) of telecommunications products for the Chinese market. This is a compulsory requirement for telecommunication devices that are connected to the public telecommunication network.
In June 2001, the first 3 product categories for the NAL approval were published. There are about 25 product categories, which include about 300 different telecommunication products that would need NAL approval. Additionally, the products would then be divided into two sub-categories, regular equipment or high-end equipment. It is important that the relevant telecommunication products are not exported to P.R. China without having the necessary NAL approval. Currently there are only 14 MIIT test labs which are authorized to provide NAL approval. Each of these test laboratories is specialized in a particular product group and all of them are accredited by the “Certification and Accreditation Administration” (CNCA).
There are four main types of applications for NAL approval: Application for regular equipment or high-end equipment, change an existing approval or the application for certificate extension.
To apply for NAL certification there are four key steps:
The first step starts with the submission of the application documents. It should be noted that the applicant must be a legal entity located in P.R. China. This is a very important consideration for foreign companies including Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan. This authorized after-sales company must be located in the P.R. China and is responsible for the complete import and export, sale and after- sales service. In the second step products tests will be performed in one of the 14 MIIT accredited test labs. In some cases, telecommunication products may need additional certification (other than NAL) including CCC certification. Applicants are advised to start the NAL test process before applying for CCC certification, since parts of the NAL test results are required in the CCC application process, therefore eliminating testing twice. In the third step of the process, a quality audit will take place. Since the MIIT does not perform these audits out of China, foreign factories must be in possession of a valid ISO 9000 certificate before starting the NAL application process. In the fourth and final step the application is approved and a certificate is issued.
If you want to learn more about the NAL approval of telecommunications products please do not hesitate to call or email us with any questions or concerns you may have. We would be happy to support you in the NAL approval process.
CFDA: More than 100 New Industry Standards released by CFDA
The China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA, chin.: 国家食品药品监督管理总局) has announced numerous new standards for CFDA certification of medical devices. According to the official announcement number 36 from October 21, 2013 (Chinese version), respectively November 26, 2013 (English version), 104 new standards were published. All of them will become effective October 1, 2014.
Industry standards (norms) are abbreviated with “YY” and define the scope, parameters and prescriptive limits for product testing required for registration of medical products and devices by the CFDA. YY Standards apply when there is no Chinese GB Standard (GB stands for Guobiao, Chinese for “National Standard”) for the product. Therefore, GB Standards supersede YY Standards. Medical devices and products may also require other certifications, e.g.
CCC (China Compulsory Certification) and CEL (China Energy Label).
Of the 104 new standards 31 are mandatory. Some of the mandatory Standards refer to ECG diagnostics systems and others to devices that are used in maternity rooms. If there is a mandatory YY standard, the product must fully comply with the standard to be approved by the CFDA for the Chinese market.
There have also been 73 recommended standards that have been released, including medical devices used in the area of anesthetics und ophthalmology. These are not mandatory at this moment, but typically will be mandatory in the future, sometimes with very short notice.
There is also mention that there are changes to two existing YY Standards, however the YY Standards and the changes have not been specified as of yet.
As soon as the CFDA publishes official announcements and more information regarding these changes, we will inform you in our “News” section on our website. Please check our website regularly for up to the date and breaking announcements and planned announcements.
Regulations and Standards that are needed for approval and registration of medical products at the CFDA are similar to the International EC (European Commission) Standards. An example would be GB 9706.1:2007 (Medical Electrical Equipment) which directly corresponds with EC 60601-1:1995. Requirements and demands of CFDA may differ from those that European or U.S. authorities would require. The decision on whether product testing can be performed in test laboratories in the manufacturing country or need to be done at an accredited test lab in China is at the discretion of the CFDA. Close, careful communications are extremely important at all phases of the certification, but most crucial during the testing phase, when communications between the applicant and the testing laboratory is time sensitive.
If you want to learn more about CFDA certification of medical devices and products, please visit the CFDA section on our website. We also provide more detailed knowledge regarding CFDA in our free brochure “CFDA China – The Booklet” that can be downloaded here.
Please do not hesitate to call or email with any questions you may have.
New GB standard and certification rules for small-and medium-sized electric rotary motors
On December 13, 2013 the National Committee for Standardization of the People’s Republic of China announced that the GB Standard 14711:2013 (published since July 2013) regarding the “Safety Requirements for Small and Medium-sized Rotating Electric Motors (motors and generators)” which will officially replace the previous GB standard 14711:2006.
Compliance to GB Standard 14711:2013 is only voluntary. Astronautic motors, traction motors, explosion proof motors, hoist and metallurgical motors will be excluded from the voluntary standard. The tests of small and medium-sized rotary electric motors must be carried out according to GB/T 5171:2002 and must also comply to the GB standard 12350:2009 for “Safety Requirements of Small-Power Motors”. Manufacturers who already hold certificates that comply with GB standard 14711:2006 must now submit a new application in compliance with GB standard 14711:2013 before their next annual follow-up audit. This adjustment of the old certificates to the new standard of certification should be completed by December 2, 2014.
If the applications are not submitted before the deadline, audits will be postponed and certificates will be cancelled by the CQC of manufacturers who fail to replace their existing certificates by December 1, 2015.
Manufacturers who voluntarily comply with the new standard before it will be made compulsory will have an advantage, since Chinese consumers are becoming more aware of the safety regulation updates and are making their purchasing decisions based on up to the date information.
Since September 1, 2012 in accordance with GB standard 18613:2012 for “Minimum Allowable Values of Energy Efficiency and Energy Efficiency Grades for Small and Medium Three-phase Asynchronous Motors” a CEL certification (China Energy Label) is also required. This GB standard was implemented to ensure that the efficiency classes of Chinese motors comply with international standards. Accordingly, the GB standard 18613:2012 refers to IEC Standard 60034-30 for “Efficiency classes of single-speed, three-phase, cage-induction motors”.
Please check the “News” section of our website regularly for up to date official announcements from the Chinese authorities, since these announcements are frequently made without any advanced notice.
You will find more information on our website under the headings CEL certification and CCC. You may also want to download our free brochure “CCC Made Easy” for more in depth information regarding the CCC certification process, requirements and the costs. You may also want to consider purchasing our book “A Brief Guide to CCC: China Compulsory Certification”, which can be ordered directly on Amazon here. We also provide more detailed knowledge regarding CEL in our free brochure “CEL-brochure” that can be downloaded here.
Please do not hesitate to call or email with any questions you may have.
CFDA: Amendments in the official “Regulations for the Supervision and Administration of Medical Devices”
The sale and/or use of some medical products and medical devices in China require prior testing and approval from the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA, Chinese: 国 家 食 品 药 品 监 督 管 理 总 局 ). If used in a doctor’s office or hospital they need to be certified by CFDA and registered in the official CFDA database. The regulatory system for registration of medical devices is based on the Provisions of the Chinese State Council and on the Normative CFDA Documents, which contain detailed rules for medical device registration and licensing. The Regulations for the Supervision and Administration of Medical Devices (Chinese: 医疗器械监督管理条例(修订草案)) from April 1, 2000 also belong to this regulatory framework.
Recently, there have been changes made in regards to these regulations.
According to an official CFDA announcement from February 13, 2014 (Chinese version), respectively February 17, 2014 (English version), the draft of the revised version is composed of 80 articles in eight chapters.
One of the key amendment changes can be found at the very beginning, of chapter one: “General Provisions”. Both the definition of medical devices and the classification criteria (regarding to the three risk classes I-III) have been modified. These changes are very important for manufacturers who currently have CFDA certification and for those who are planning to do so, since the definition changes may affect the need for certification. Devices or products that once needed certification may no longer need it, whereas devices or products that previously did not need certification my now need it.
Adaption of the classification criteria might also have a deep impact for applicants of CFDA certification. Up to this point, the criteria were based on the European Council Directive 93/42/EEC. For each product class (I-III) the CFDA requires specific administrative procedures, product tests and/or clinical trials. Class I devices may only be required to pass relatively simple administrative and approval procedures to seek authorization for Chinese market, while class II and III devices need product testing and possible clinical trials. Due to the upcoming adjustments required approval procedures may change in the future. Depending on how the device or product is reclassified the severity of the tests may either increase or decrease, possibly pushing a device into clinical trials where it previously only needed simple lab tests, or vice versa.
Besides the amendments mentioned above, new restrictions and provisions have been defined in the course of changing the regulations. The modifications affect the following areas:
- Quality supervision and risk control during production process of medical devices
- Adverse event monitoring, retracing and recall of medical devices
- Application for licenses and permissions for distribution of medical devices in China
- Punishments and fines for illegal activities
The draft amendment to the Regulations for the Supervision and Administration of Medical Devices was adopted in an executive meeting of the Chinese State Council on February 12, 2014.
Until now, the updated regulations have neither been promulgated nor officially implemented, however the CFDA has announced that they will be enforced in the near future.